The Importance of Using Child Restraint Systems (CRS) in Malaysia
1. Introduction
Child safety in vehicles is an important aspect in efforts
to reduce the rate of injuries and deaths due to road accidents in Malaysia.
Along with the increase in the number of private vehicles and traffic density,
the risks to child passengers also increase, especially when appropriate safety
measures are not followed. In this essay of my assignment, I will present a
topic that is still a topic of conversation in current issues, namely the role
of tax incentives in the ownership of child safety seats. Child Restraint
Systems (CRS) have been scientifically proven to reduce the level of serious
injuries and the risk of death in the event of an accident. However, the level
of ownership and use of CRS among Malaysian society is still at a moderate
level and is not yet comprehensive.
Nowadays, the Malaysian government has started to
strengthen its road safety policy by enforcing the use of CRS. This is in line
with the Malaysian Road Safety Plan and commitment to international standards.
However, the main challenge identified is the cost of purchasing CRS which is
considered high by some low- and middle-income groups, thus becoming one of the
factors causing the CRS ownership gap, despite the increasing awareness of its
importance. Therefore, the Malaysian government has taken tax incentives to
educate and take the lead. In this way, it is seen as an effective mechanism to
encourage the ownership and use of child safety seats. So,
let's discuss my topic, which is the role of tax incentives in child safety
seat ownership.
2. Importance of Using Child Restraint Systems (CRS) in Malaysia
- Child safety in vehicles is an important component of road safety, especially in Malaysia which still records a high rate of road accidents.
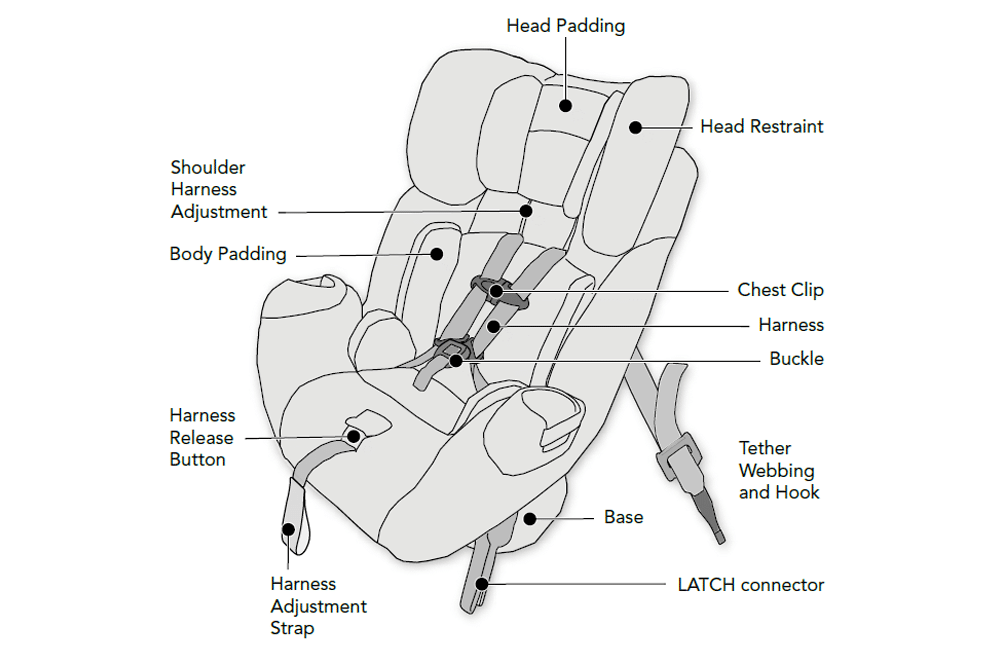
- Child Restraint Systems (CRS) are specially designed according to the age, weight and height of the child to provide more effective protection than regular seat belts.
- The use of CRS can reduce the risk of serious injury and death of children, especially injuries to the head, neck and spine during collisions or emergencies.
- The implementation of CRS laws in Malaysia shows the government's commitment to protecting child safety, but the level of compliance still needs to be improved.
- Factors such as lack of awareness, parental negligence and the cost of purchasing CRS are certainly the main challenges in the implementation of CRS use in a comprehensive manner.
- Road safety education and ongoing public awareness campaigns are very important to increase public understanding of the importance of correct and consistent use of CRS.
- The use of CRS also contributes to the formation of a safer, disciplined and responsible driving culture among road users.
- the use of CRS is an effective preventive measure in protecting children's lives and reducing the impact of road accidents in Malaysia.
3. Issue Analysis
- Child safety is supported through a legal framework (Road Transport Act 1987)
- The use of CRS has been mandatory since 1 January 2020 for children under 12 years old / <36 kg / <136 cm
- CRS must comply with international standards UN R44 and UN R129 (i Size)
- Weak enforcement means that the level of CRS usage is still low
- ASEAN NCAP supports child safety through COP ratings and the promotion of ISOFIX features. ISOFIX is a child safety seat (CRS) installation system that is attached directly to the vehicle structure to ensure the CRS is installed more firmly, safely and correctly.
- CRS awareness/use increased after mandatory law in 2020, but not consistent
- Highest reported CRS use: 2020 (44–50%) and 2024 (45%)
- CRS usage declined again in 2022 & 2025 (~30%)
- Child accident & mortality figures remain high despite legislation
- 2025 recorded 714 child deaths, indicating ongoing safety issues
- Data sourced from MIROS, PDRM, MOT & national media.
- The Malaysian government has enacted and enforced mandatory CRS regulations through legislation under the Road Transport Act to improve the safety of children in vehicles.
- Enforcement of CRS laws is carried out by relevant agencies such as the Royal Malaysian Police (PDRM) and the Road Transport Department (JPJ) through road inspections and summons for violations.
- The government also conducts continuous public awareness campaigns through mass media, social media and community programs to educate parents about the importance and proper use of CRS.
- The Malaysian Institute for Road Safety Research (MIROS) is responsible for conducting research, providing technical guidelines and disseminating data-based information on the effectiveness of CRS in reducing child injuries and deaths.
- The government encourages strategic collaboration with the private sector, vehicle manufacturers and non-governmental organizations (NGOs) in promoting the use of CRS through educational programs and donations of safety equipment.
- Initiatives such as exemptions or reductions in sales tax for certain CRSs as well as financial incentives are proposed to reduce the cost burden on low-income groups.
- Road safety education related to CRS is also implemented through education and advocacy programs, including safety talks and early exposure to parents and guardians.
- the government's efforts in promoting the use of CRS aim to create a more caring and responsible road safety culture, especially in protecting children as vehicle passengers.
In conclusion, the use of child safety seats is an
important step in protecting the lives and safety of children while in
vehicles. Although the law on CRS has been implemented in Malaysia, the level
of compliance is still low and has not achieved the desired goals of our country.
Therefore, I suggest that future improvements should focus on more consistent
enforcement, increased public awareness, and the provision of tax incentives or
financial assistance to ease the cost of purchasing CRS in the Malaysian
market. With these measures, we can encourage the ownership and use of CRS more
widely among Malaysians. With this more comprehensive approach, road safety
policies in Malaysia related to children can be implemented more effectively,
thereby reducing the rate of injuries and deaths of children due to road
accidents, especially cars.


Ilmu yang sangat bermanfaat ☺️
ReplyDelete